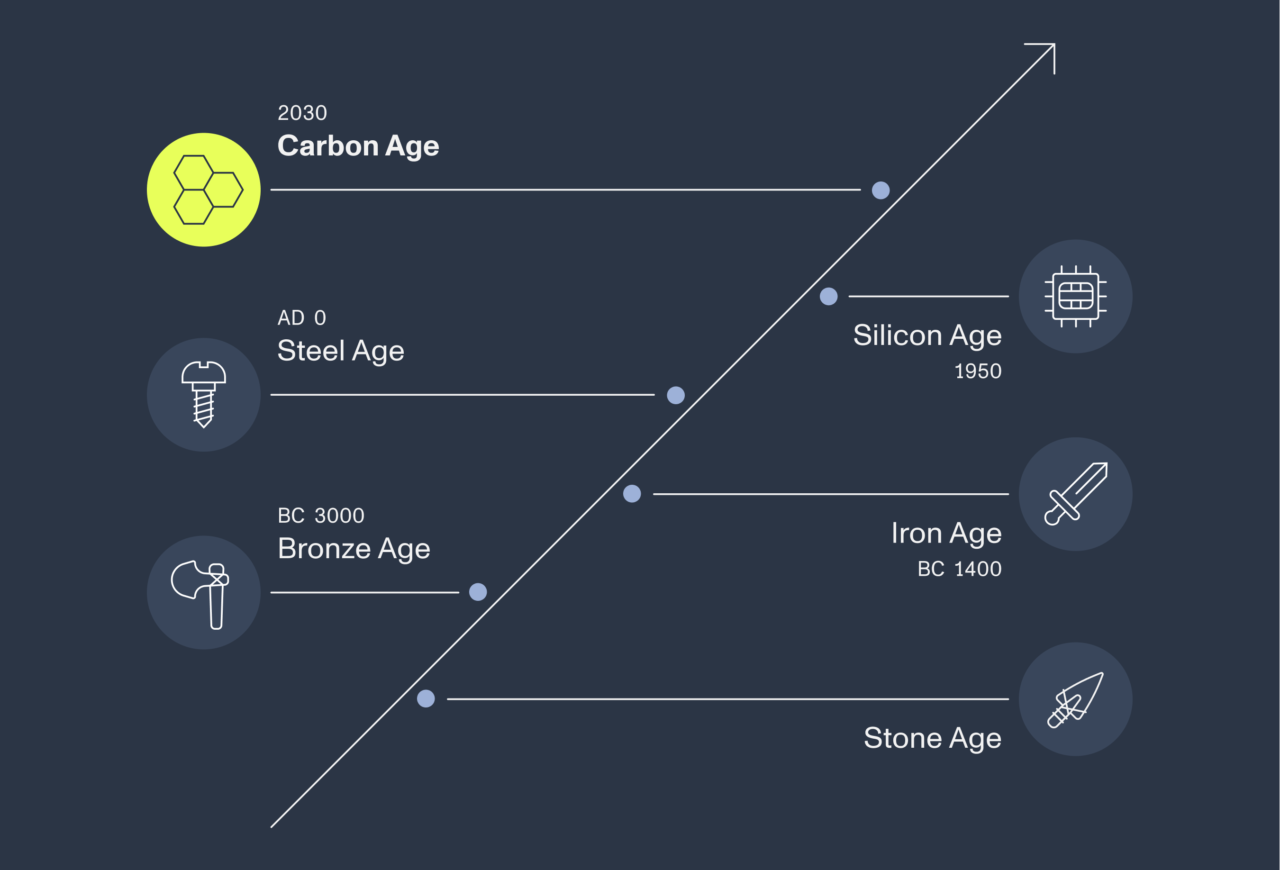
The carbon age: repurposing carbon emissions for good
Carbon nanotube manufacturing through chemical vapor deposition (CVD) process involves utilizing carbon-based gases as a raw material. This offers an exciting opportunity to reuse carbon emissions from industrial sources as a feedstock for the synthesis of carbon nanotubes (CNTs).
Carbon emissions are a readily available byproduct of various industrial processes, including those from local power plants that contribute to global warming. By repurposing these emissions, we can mitigate their impact on the climate while simultaneously creating carbon nanotubes in a more sustainable manner.
Traditional materials, such as steel, aluminum, and copper typically rely on mining or far-off oil refining processes. For example, the carbon emissions generated during silicon mining and refining are not only substantial but also harmful to the local ecosystems. These materials often require extraction and transportation of raw materials, which can be resource-intensive and energy-consuming. In contrast, using carbon emissions from local sources as a building block is more resource-efficient and can lead to smaller overall environmental impact.
Carbon nanotubes have various potential uses, including electronics, energy storage and composites. One key benefit of using nanomaterials is that you need only a tiny amount to achieve equal or better performance in the application. For example, when used as an additive in composites, achieving the same effect often requires just 0,01% of CNTs compared to 15-35% for metal fillers or 20-40% for carbon black, resulting in significant savings in material resources. Furthermore, carbon nanotubes are exceptionally lightweight, being only half as dense as aluminum. This helps reduce the application’s overall weight.
“Carbon nanotubes have the potential to enable several cleantech solutions, delivering higher performance and a lower carbon footprint. Utilizing carbon as a building block instead of releasing it into the climate is the foundation of the Carbon Age.”
Ilkka Varjos, CTO, Canatu
Using carbon nanotubes in car manufacturing creates lighter vehicles with better efficiency, leading to longer ranges and reduced emissions. One example is our CNT film heaters which are used for deicing camera and LiDAR sensor covers. These heaters require 40% less energy compared to the traditional heating wires, supporting car manufacturers in their quest to save energy everywhere.
When assessing the environmental impact of a solution, various factors come into consideration. Nanocarbon materials, such as carbon nanotubes, possess remarkable potential to initiate a cascade of positive outcomes. Carbon nanotubes have the potential to enable several cleantech solutions, delivering higher performance and a lower carbon footprint. Utilizing carbon as a building block instead of releasing it into the climate is the foundation of the Carbon Age.
Contact

Send us a message
Related content
Carbon is versatile, future-proof and available everywhere. With nanotech we extract the unique properties of carbon, making it attractive across different applications. Learn how breakthroughs can be enabled with more responsible materials and smaller quantities for massive impact. Learn more.

We are all about making things future-proof. Whether working with partners on new solutions or developing our operations, a more sustainable future guides our actions. Our sustainability in action.
For the second consecutive year, Canatu has been awarded a Gold medal in corporate social responsibility by EcoVadis. This places us in the top 3% for social responsibility performance among all companies assessed. The assessment focuses on 21 sustainability criteria that are grouped into four themes: environment, labor & human rights, ethics, and sustainable procurement. See press release.

Canatu has shifted from fossil fuels to renewable energy part of our sustainability strategy to decarbonize production by 2035. This transition is primed to reduce our CO2 emissions from electricity staggering 94%, while reducing our total CO2 emissions by 60%. See news release.